Showing all 2 results
What is the use of Demerol?
Demerol is meperidine hydrochloride oral tablets in the strength of 50mg and 100mg. Meperidine hydrochloride is a white crystalline opioid substance readily soluble in water. Demerol is also available as a pleasant-tasting, banana-flavored, non-alcoholic solution containing 50mg of meperidine hydrochloride per 5ml (10mg/ml).
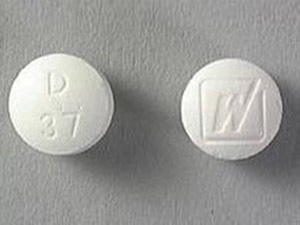
Inactive ingredients of Demerol tablets are dibasic calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate, stearic acid, starch, and talc. Demerol tablets are white-colored, round and convex with an imprint of stylized “W” on one side and “D” with “35” (50mg) or “37” (100mg) on the other side.
How to Demerol uses?
Buy Demerol online to treat acute pain. Being an opioid, Demerol has a high potential for addiction, abuse, and misuse. Due to this, it is recommendable to order Demerol online and use it only for the patients for whom alternative treatment options such as other less potent opioids, mixed agonist opioids, or non-opioids are either not tolerated, or inadequate to provide sufficient analgesia.
Demerol side effects
Severe side effects associated with Demerol use include:
- Seizures
- Fatal respiratory depression
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Serotonin syndrome
- Gastrointestinal reactions
- Withdrawal
- Severe hypotension
- Interaction with CNS depressants such as benzodiazepines
- Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome
- Addiction, abuse, and misuse.
The significant dangers of Demerol use are respiratory depression, and circulatory depression, circulatory arrest, cardiac arrest, shock, or death, in case of overdose.
Other adverse reactions of Demerol include:
- Nervous System: headache, weakness, mood changes, tremor, agitation, severe convulsions, disorientation, hallucinations, confusion, and visual disturbances.
- Gastrointestinal: constipation and dry mouth.
- Cardiovascular: bradycardia, tachycardia, palpitations, syncope, and hypotension.
- Allergic: urticaria, skin rashes, sweating, and hypersensitivity reactions.
- Serotonin Syndrome
- Adrenal Insufficiency
- Androgen Deficiency
Demerol dosage
Initial Dose: Initiate treatment with 50mg to 150mg orally given every 3-4 hours as needed.
Reduce the initial dose by 25-50% if using concurrently with phenothiazines and other tranquilizers.
The maximum total daily dosage is 600 milligrams per day.
Titration and maintenance: Individually titrate the doses to get adequate pain relief and minimum side effects. If sufficient analgesia is not achievable through 600mg per day dose, discontinue the treatment with Demerol by slowly tapering doses, and select some alternative pain medication.
Continually reassess a patient for adverse reactions as well as addiction and abuse.
If pain escalates after dosage stabilization, identify the source of increased pain instead of increasing Demerol dosage.
Discontinuation: When a patient no longer requires Demerol treatment, reduce the dose gradually, by 25% to 50% every 2-4 days, while monitoring the patient for symptoms of withdrawal. If signs of withdrawal appear, raise the dose to precede level and decrease more slowly. Never abruptly discontinue the treatment of Demerol in physically dependent patients.
Precautions
Take the following precaution to avoid any adverse or life-threatening effects of Demerol:
- Avoid dosing errors while taking the medication as it has a risk of accidental overdose and death. Take the doses exactly as prescribed by a doctor.
- Demerol is a schedule II substance, thus exposes users to the risk of addiction and abuse. Do not take the medication if you have a history of drug abuse.
- Demerol being an opioid, has a high risk for life-threatening respiratory depression. Avoid overdose and incorrect dosing.
- The use of Demerol during pregnancy can cause withdrawal in the neonate. Consult a doctor before taking it during pregnancy.
- Using Demerol with central nervous system depressants such as benzodiazepines or alcohol can cause severe sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and even death.
- Demerol has a fatal interaction with Monoamine Oxidize Inhibitors (MAOs). It contraindicates in patients receiving MAOs and other such agents.
- Do not give Demerol to elderly or debilitating patients, or patients with chronic pulmonary disease. It causes fatal respiratory depression and other severe side effects in such patients.
- Do not use Demerol concurrently with serotonergic drugs as it can cause serotonin syndrome.