Anxiety is a common mental health condition affecting millions worldwide. Is Xanax Right for Anxiety ? While occasional stress is normal, persistent anxiety can disrupt daily life, relationships, and work performance. Understanding whether medications like Xanax are appropriate requires knowledge of the symptoms, diagnosis, and safe treatment strategies. This guide provides an in-depth look at anxiety symptoms, signs of anxiety disorders, and medical assessment for anxiety, helping you make informed decisions about whether Xanax or alternative treatments may be right for you.
Understanding Anxiety: More Than Just Stress
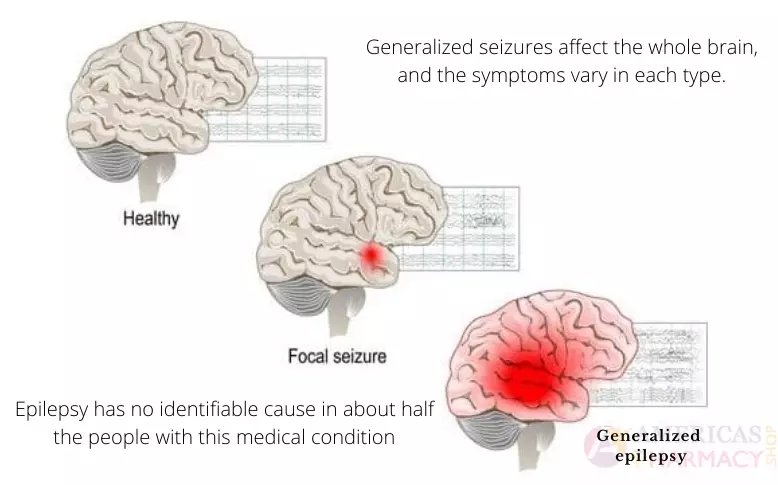
Anxiety is often misunderstood as simple worry or stress, but it is far more complex. Symptoms range from excessive fear and restlessness to physical manifestations such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, or muscle tension. Recognizing signs of anxiety disorders early is crucial for effective treatment.
Medical professionals categorize anxiety into multiple disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Each disorder has unique triggers, intensity, and impact, which influence the decision to use medications like Xanax. Comprehensive anxiety management guides often combine lifestyle adjustments, therapy, and, in some cases, medication.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety
Identifying anxiety symptoms is the first step toward relief. Individuals may experience persistent worry, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating. Physical symptoms can include trembling, shortness of breath, and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Recognizing these symptoms early allows for timely medical assessment for anxiety. Knowing when anxiety crosses the threshold from occasional stress to a clinically significant disorder helps you and your healthcare provider determine the appropriate treatment steps for anxiety, including the potential role of Xanax or other medications.
How Doctors Diagnose Anxiety
The process of how doctors diagnose anxiety involves a thorough evaluation of both psychological and physical health. Healthcare providers conduct interviews, questionnaires, and sometimes lab tests to rule out other conditions. They assess the severity, duration, and impact of symptoms on daily life.
A proper Xanax medical evaluation ensures that the medication is prescribed only when necessary and that alternative safe anxiety treatment options are considered. This structured approach prevents misuse of benzodiazepines for anxiety and promotes a holistic treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
When Is Xanax Prescribed?
Xanax, a type of benzodiazepine, is typically prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety or panic attacks. Doctors may consider prescribing it when other treatments, such as therapy or SSRIs, are insufficient. Common when is Xanax prescribed scenarios include acute episodes of panic, extreme situational anxiety, or immediate symptom management.
While effective, Xanax carries risks of dependency and side effects, making it essential to use under strict medical supervision. A careful doctor consultation for anxiety helps evaluate whether Xanax is suitable and what dosage and duration are safe for the patient.
Understanding Xanax: Benefits and Risks
Xanax can provide rapid relief for intense anxiety symptoms. Its primary benefit lies in its ability to calm the nervous system, reduce panic episodes, and improve sleep disrupted by anxiety. However, risks include drowsiness, dizziness, memory impairment, and potential for addiction with prolonged use.
It’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the risks and explore short-term anxiety medication strategies. Doctors often recommend a limited duration for Xanax use while integrating therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative medications for long-term management.
Safe Anxiety Treatment Options
Not everyone with anxiety requires Xanax. Safe anxiety treatment options include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, lifestyle modifications, and non-benzodiazepine medications. These approaches aim to address the root causes of anxiety rather than just the symptoms.
Understanding the full spectrum of anxiety relief medications ensures that patients can choose approaches that align with their health goals. Combining therapy with lifestyle changes often results in long-lasting improvements and reduces the need for dependency-prone medications like Xanax.
Best Place For Buy Xanax Online – AmericasPharmacy.shop
Alternatives to Xanax
Several effective alternatives to Xanax are available for anxiety management. SSRIs, SNRIs, beta-blockers, and natural supplements such as CBD or magnesium can offer relief without the risks associated with benzodiazepines.
Additionally, techniques like meditation, breathing exercises, and structured anxiety management guides can complement medication or, in some cases, replace it entirely. Patients should discuss these alternatives during a doctor consultation for anxiety to ensure safety and efficacy.
Steps to Take Before Considering Xanax
Before exploring the option to buy Xanax online or seek prescriptions, patients should undergo a comprehensive medical assessment for anxiety. Steps include documenting signs of anxiety disorders and frequency of symptoms, consulting a licensed healthcare provider to discuss potential short-term anxiety medication options, evaluating lifestyle factors and considering safe anxiety treatment options, and understanding the risks and benefits of benzodiazepines for anxiety.
Following these steps ensures that the decision to use Xanax is informed, safe, and tailored to the patient’s individual needs.
The Role of Online Access: What to Know
The internet offers the convenience to buy Xanax online, order Xanax online, or search for where to buy Xanax online, including options claiming buy Xanax online No Rx. While accessibility may seem attractive, purchasing Xanax without a prescription poses serious legal and health risks.
It is vital to prioritize safety and consult a doctor before obtaining Xanax online. A legitimate Xanax medical evaluation ensures proper dosage, reduces side effects, and prevents dependency. Remember, convenience should never compromise safety when managing anxiety.
Conclusion
Deciding if Xanax is right for anxiety requires careful evaluation of symptoms, severity, and treatment goals. While Xanax can provide rapid relief for acute anxiety or panic attacks, it carries potential risks and should be used only under medical supervision.
A comprehensive approach that includes a proper doctor consultation for anxiety, safe anxiety treatment options, lifestyle changes, therapy, and alternative medications often delivers the best long-term results. Understanding your options empowers you to manage anxiety effectively while minimizing risks. Whether you choose Xanax or other strategies, informed decisions and professional guidance remain key to achieving lasting anxiety relief.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Xanax right for everyone with anxiety?
Ans : No. Xanax is generally reserved for severe anxiety or panic episodes. Doctors often recommend therapy or alternative medications first.
How do doctors diagnose anxiety?
Ans : Doctors conduct interviews, questionnaires, and sometimes lab tests to rule out other causes and evaluate severity and frequency of anxiety symptoms.
Can I buy Xanax online safely?
Ans : Only through licensed and verified pharmacies with a prescription. Avoid websites offering buy Xanax online No Rx as it can be illegal and unsafe.
What are alternatives to Xanax?
Ans : Alternatives include SSRIs, SNRIs, beta-blockers, natural supplements, CBT, mindfulness practices, and lifestyle changes.
What are the risks of Xanax?
Ans : Risks include dependency, drowsiness, dizziness, and memory impairment. It should only be used short-term under medical supervision.
What are the steps before starting Xanax?
Ans : Steps include documenting signs of anxiety disorders, consulting a doctor, considering safe anxiety treatment options, and understanding risks and benefits.
Buy Xanax Online – Use Coupon Code ” SAVE10 ” Get Best Offer