Debilitating depression
In 2021, an estimated 14.9 million adults aged above 18 in the USA had debilitating depression with severe impairment in the past year. This number represented 6.0 percent of all adults in the USA. Please read this blog to understand debilitating depression in detail.
What is debilitating depression?
Debilitating depression is when the symptoms of major depression are so severe or prolonged that a person can’t function normally in one or more areas of their life. For instance, debilitating depression may make it impossible to keep up with housework, basic hygiene, a job, or normal relationships with family and friends. There are some pretty severe consequences of untreated debilitating depression, including suicide. Therefore, it is essential to get treatment for debilitating depression.
What are the symptoms of debilitating depression?
Some symptoms that you have debilitating depression can include:
- Not bathing or showering for days or weeks
- Neglecting hygiene, wearing dirty clothes, and not brushing hair
- Being completely unable to function in school or at work
- Feeling extremely agitated and guilty
- Having sleep disturbances
- Forgetting to eat or consuming only whatever junk food is available
- Noticeable slowing of your ability to think or do remotely active tasks, even getting up and walking around your house
- Psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations or delusions and becoming physically immobile
One must address this severe and debilitating depression since it can cause severe complications, such as substance abuse, physical injuries due to self-harm, malnutrition, failing at school or loss of a job, physical illnesses, social isolation, and damaged relationships.
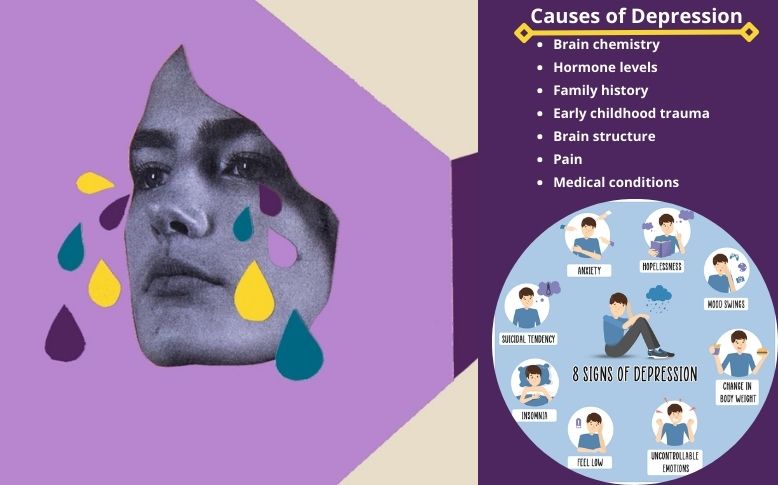
What are the causes of debilitating depression?
Debilitating depression is one of the most common mental illnesses in the USA. Research suggests that genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors can be responsible for debilitating depression. There are several potential causes of debilitating depression, and some factors may combine to trigger symptoms. Factors that can increase an individual’s risk of developing debilitating depression are:
- a personal or family history of debilitating depression
- certain physical illnesses, like diabetes, heart disease, and Parkinson’s disease
- significant life changes, including stress and trauma
- specific medications
Treating and Managing debilitating depression
Everybody experiences depression in unique ways, even with typical symptoms. Some people have less frequent states of depression or more mild depressive moods. These moods may debilitate others. People with debilitating depression might not be able to function, struggling to do even the basic daily tasks such as bathing and getting dressed. This degree of depression is not something a person has to live with for long. If you or someone you care for is struggling with debilitating depression, seek treatment. Debilitating depression feels hopeless, but there is hope.
There is no cure for debilitating depression, but with the correct medical treatment and therapy, you can live with depression, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of future episodes. Even for the most debilitating cases of depression, treatments can be effective. The treatment for patients with debilitating depression is usually similar to the treatment for other kinds of depression. Below, this blog shares some common treatments for individuals with debilitating depression.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a standard treatment for debilitating depression. Psychotherapy can include talk therapy, which involves patients with debilitating depression attending regular sessions with a therapist to share how they feel. Psychotherapy can allow individuals to learn ways to adjust to situations that worsen their depression symptoms.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (or CBT) is another type of psychotherapy that medical experts use to treat debilitating depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy focuses on how beliefs, thoughts, and attitudes can affect people’s behaviors and feelings. Cognitive-behavioral therapy uses a hands-on and practical approach, with a therapist interacting with the person to modify their patterns of behavior and thinking. This modification allows the individual to achieve a beneficial change in their mood and how they live their lives.
Medications
Doctors and mental health experts usually prescribe antidepressants for people with debilitating depression. These medications regulate chemicals and hormones in the brain that contribute to an individual’s mental health. The drugs aim to modulate mood and behavior, and both relieve the debilitating depression symptoms and prevent them from coming back.
- Serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (i.e., SNRIs) are common antidepressant drugs that doctors prescribe to treat debilitating depression. Examples of SNRIs are desvenlafaxine (Pristiq), duloxetine (Cymbalta), and venlafaxine (Effexor).
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (or SSRIs) are another common medication for the treatment of debilitating depression. Examples of SSRIs are citalopram (Celexa), paroxetine (Paxil), fluoxetine (Prozac), and sertraline (Zoloft).
Electroconvulsive therapy (or ECT)
ECT is a treatment for people with debilitating depression. ECT is an option for patients who don’t respond to medication or psychotherapy. ECT takes place under general anesthesia. While the individual is under general anesthesia, a medical team places electrodes on the scalp in precise locations. Then they stimulate their brain with controlled and brief electrical pulses. This stimulation leads to a small seizure within their brain that lasts about one minute. ECT aims to cause changes in the brain’s chemistry to improve depression symptoms and other mental health conditions.
Other treatments for debilitating depression
People can also try to reduce debilitating depression symptoms in other ways. A mental health doctor can advise on methods to try, which can include:
- alternative approaches, such as acupuncture
- light therapy
- regular exercise
- nutritional changes
Debilitating depression and anxiety
The chance of acquiring anxiety is much higher when debilitating depression already exists. Nearly half of those with debilitating depression also suffer from persistent and severe anxiety. People who have debilitating depression feel anxious and tense often. One can easily trigger the other, with anxiety usually preceding debilitating depression.
Summary
Debilitating depression is a severe mood disorder that causes people to have a persistent feeling of sadness. People usually describe debilitating depression as crippling. Debilitating depression can make a person feel constantly depressed or low. It can also lead to feelings of worthlessness and guilt and the inability to feel pleasure in things that an individual would usually find pleasurable. Debilitating depression can also prevent sufferers from completing regular daily tasks like eating, working, and sleeping.
Common treatments for debilitating depression involve psychotherapy and a range of antidepressant medicines. These treatments can be pretty effective and work well to manage symptoms of debilitating depression.