Overview of Depression
Major depressive disorder, popularly known as depression in general term, is a mood disorder that makes an individual feel constant sadness or lack of interest in life. Data from CDC estimates that 18.5 % of adults in the United States had depression symptoms in any given two-week period in 2019.
Sadness and depressed feelings are ordinary in everyone’s life at times, and it is a normal reaction to the changes and challenges of life. But when this condition turns into a feeling of intense sadness, including thoughts of hopelessness, helplessness, and worthlessness, which last for several weeks and keep you from living your life, it may be something more than ordinary sadness. It is clinical depression.
It strikes people in different ways. It may interfere with the daily working routine, resulting in lower productivity and lost time. It can also trigger some chronic health problems and influence relationships, and the medical conditions that can worsen due to depression include asthma, arthritis, cancer, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and diabetes.
Suppose you wonder if treating this mental condition is possible; yes! It is a treatable problem. This blog will help you understand more about Depression and its treatment.
What are the signs and symptoms of Depression?
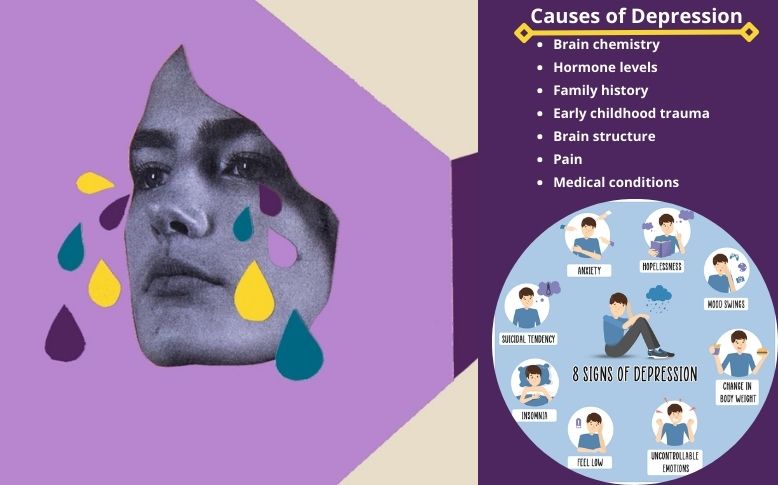
It can cause various symptoms ranging from constant sadness to feeling “blue” or more. Some symptoms of depression affect your mood, while others can affect your body.
General signs and symptoms of depression
It is not the same for everyone; symptoms can vary in severity, how long they last, and how often they happen. If you face some of the depression signs and symptoms nearly every day for at least two weeks, you may have depression:
- feeling anxious, sad, or “empty,” crying a lot
- feeling worthless, pessimistic, bothered, hopeless, angry, or annoyed
- loss of interest in activities once you used to love doing
- difficulty remembering, concentrating, or making decisions
- feeling fatigued or decreased energy
- sleeping problems, appetite, or weight changes
- chronic physical pain with no particular reason, such as digestive problems, headaches, cramps, aches, or pain
- thoughts or self-harm, suicide, death, suicidal thoughts
Depression symptoms in males
- Mood: aggressiveness, anger, anxiousness, irritability, or restlessness
- Changes in behavior: loss of interest, feeling tired quickly, no longer feeling pleasure in the activities you used to love once, drinking excessively, using drugs, thoughts of suicide, or engaging in high-risk activities
- Cognitive abilities: difficulty completing tasks, inability to concentrate, or delayed responses during conversations
- Sexual interest: lack of sexual performance or reduced sexual desire
- Sleep patterns: restless sleep, insomnia, excessive sleepiness, or not sleeping at all
- Physical well being: pain, fatigue, digestive problems, or headache
Buy Xanax Online : AmericasPharmacy.shop
Depression symptoms in females
- Mood, such as irritability
- Changes in behavior: loss of or no interest in activities, thoughts of suicide, or withdrawing oneself from social engagements
- Emotional well being: feeling sad or empty, hopeless, or anxious
- Cognitive abilities: thinking or talking more slowly
- Sleep patterns: difficulty sleeping or excessive sleeping
- Physical well being: digestive problems, loss of energy, weight loss or gain, or changes in appetite
What are the different types of Depression?
Some of the known depression types may include:
- Unipolar major depression
- Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, when an individual gets very angry, cranky, and often display intense outbursts
- Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia), a depression lasting for more than two years
- Substance-induced mood disorder (SIMD), the symptoms usually occur when you are taking a medicine or consuming alcohol or after you stop taking any substance
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder, when a woman goes through severe mood problems before periods, is much more intense than the typical premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
What are the causes of Depression?
Causes of depression can range from biological factors to circumstantial factors. But the common causes include:
- Brain chemistry: A chemical imbalance in the brain parts that manage thoughts, mood, appetite, sleep, and behavior in people who are dealing with depression.
- Hormone levels: It is one of the common it causes in females. Changes in female hormones progesterone and estrogen during various periods in life such as perimenopause, menstrual cycle, postpartum period, or menopause may raise the risk of depression in women.
- Family history: You are at a higher risk if you have a family past of it or other similar mood disorders.
- Early childhood trauma: Some events affect how your body reacts to fear and other stressful situations.
- Brain structure: The risk of it is higher if your brain’s frontal lobe is less active.
- Substance use: If you have a history of substance use disorder or alcoholism, it can affect your risk.
- Pain: People who feel chronic physical pain or emotional pain for prolonged duration are significantly more prone to develop it.
- Medical conditions: Specific medical conditions may put you at higher risk, such as insomnia, chronic illness, Parkinson’s disease, chronic pain, heart attack, and cancer.
How to deal with Depression?
You may successfully manage it by using one form of treatment persistently, or you find a combination best suitable for you. Some of the common categories of medications may include SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), noradrenaline and dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs), and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists.
Psychotherapy
Conversing with a therapist can help you cope with specific negative feelings and benefit from group therapy sessions or family. It is also known as “talk therapy” and is famous as an effective treatment. Psychotherapy is often prescribed together with pharmaceutical treatment. A combination of an effective drug and psychotherapy can come out as a catalyst in your it treatment.
FAQ
Qus1: What are some natural remedies that may help with anxiety and depression?
Ans:Common natural approaches include regular physical activity, mindfulness practices such as meditation or yoga, maintaining a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress-reduction techniques. Some people also explore herbal supplements like chamomile or ashwagandha, though results can vary and professional guidance is recommended.
Qus 2: Can lifestyle changes really improve anxiety and depression symptoms?
Ans:Yes, lifestyle changes can play a supportive role. Consistent exercise, limiting alcohol and caffeine, building healthy routines, and staying socially connected may help improve mood and emotional resilience over time. These strategies are often used alongside professional care rather than as replacements.
Qus 3: Are natural remedies safe for everyone?
Ans:Not always. While many natural methods are generally well tolerated, some supplements and practices may interact with medications or underlying health conditions. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement or alternative approach.
Qus 4: How long do natural remedies take to show results?
Ans:The timeline varies by individual and method. Some people notice gradual improvements within a few weeks, especially with consistent habits like exercise or mindfulness. Natural approaches usually require patience and ongoing commitment.
FAQ 5: Can natural remedies replace medical treatment for anxiety or depression?
Ans: Natural remedies are best viewed as supportive options, not substitutes for professional diagnosis or treatment. For moderate to severe anxiety or depression, licensed healthcare providers can help determine whether therapy, medication, or a combined approach is appropriate.
Visit AmericasPharmacyShop :- Get Biggest Disscount On First Order