An overview of illness
Hypothermia is a severe medical condition that occurs when an individual’s body temperature drops below 95 degrees. This drop in temperature can result in significant health complications, including death. Hypothermia is a problematic issue as it affects the ability of the person to think clearly. Also, it can reduce your likelihood of asking for medical help. You can experience this issue if you experience cold temperatures for an extended duration.
While your body’s normal metabolic processes generate heat, cold wintry weather can make the body lose more heat than usual. When such cold wind strikes, the core temperature drops. Hypothalamus: is a significant structure in the brain responsible for regulating body temperature. Some findings indicate that when you are exposed to cold, the hypothalamus raises your body’s temperature through specific measures, including increased muscle toning and shivering.
However, your body will eventually overwhelm with continuous exposure to cold, and the shivering will stop. Multiple body organs may stop their regular functioning in this situation, ultimately resulting in death. And, this makes hypothermia a hazardous condition.
Symptoms of hypothermia
Symptoms of least severe or mild hypothermia include:
- tiredness, shivering, with a body temperature of 90 to 95 degree
- nausea, hunger, rapid heart rate, unclear speech
- increased muscle tone and blood pressure
- dry skin that is paler than usual, frequent urination
- loss of control of body movements
- poor judgment, decline in memory and thinking ability
Usually, shivering stops when the temperature ranges between 86 to 90 degrees. Other symptoms of moderate hypothermia may include:
- lethargy, continuous reduction in thinking ability
- body temperature between 82 to 90 degrees
- low blood pressure, less responsive enlarged pupils
- slow heart rate and breathing rate
- increased susceptibility to irregular heart rhythms
- paradoxical undressing (removal of clothes)
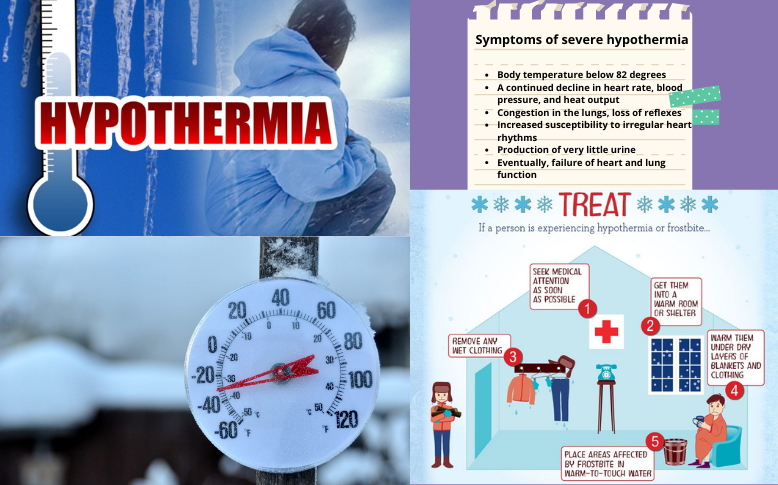
Symptoms of severe hypothermia include:
- continuous reduction of blood flow to the brain, making you unresponsive
- body temperature below 82 degrees
- a continued decline in heart rate, blood pressure, and heat output
- congestion in the lungs, loss of reflexes
- increased susceptibility to irregular heart rhythms
- production of very little urine
- Eventually, failure of heart and lung function
What causes hypothermia?
The primary reason for hypothermia is cold weather. When the body faces frigid temperatures, it starts losing heat more rapidly than it can produce. Staying in cold water for an extended period can also cause these effects. In such situations, the inability of your body to produce adequate heat becomes extremely dangerous. The temperature of your body can drop drastically low in a brief period.
Exposure to temperatures your body is not used to or colder than usual can also cause this condition. For example, if you get into a cold, fully air-conditioned room right after being outside, you put your body at the risk of losing excessive body heat in a short span.
Hypothermia in babies
According to the CDC, hypothermia in babies has different symptoms from adults. Babies are more likely to experience low energy with bright red and cold skin. As hypothermia worsens through the stages, the symptoms become more severe and dangerous. To prevent hypothermia in babies, you must dress them warmly and limit their exposure to places with cold temperatures.
Long term effects of hypothermia
To prevent the long-term effects of this medical issue, you need to get immediate medical attention. The more your wait, the longer its effects will arise and remain. If left untreated, hypothermia can further lead you to heart attack, kidney failure, liver damage, or even death. Other long term complications associated with this condition include:
- frostbite, or tissue breath, is a common complication when body tissues freeze
- gangrene, or tissue destruction
- chilblains, or damage in nerve and blood vessel
- trench foot, destruction of nerve and blood vessel due to water immersion
What should be hypothermia prevention?
To prevent hypothermia, you should follow these preventive measures:
- have a look at the day’s weather forecast before stepping out of the house, and dress accordingly
- avoid alcohol consumption and drinking caffeinated beverages as they fasten heat loss
- Set up the home thermostat at 68 degrees or more, and dress warmly
- to prevent wind drafts, place rolled towels underneath the doors,
- check on older adults in your neighborhood, and ensure they have enough heat and food
In winter, unexpected events such as home power outrages and exhaustion of gas while driving can occur, posing a danger of hypothermia. Experts recommend keeping emergency survival kits at home and in your vehicle to come out safe from these events.
Home survival kits may include an emergency heating source, extra packed food and water, a fire extinguisher, and a smoke detector. While the car survival kit may consist of extra clothing to keep dry, sleeping bags and blankets, a water container, high-calorie (nonperishable) food, and waterproof matches.
Specific drugs, including psychiatric medications, are likely to increase the risk of hypothermia in an individual. It would help if you considered asking your medical healthcare provider whether the drug they are prescribing could increase the risk of hypothermia.
Which of the following is a proper way of hypothermia treatment?
This condition is a medical emergency, so if you suspect that you or someone is going through hypothermia, call for immediate medical help. The goal of any treatment in this problem is to increase your body’s temperature to a normal range. You may try the following methods until medical help reaches:
Remove wet clothing
Remove the affected person’s wet clothes. And if necessary, cut off the clothes while avoiding moving the individual. Cover them with warm pullovers or blankets, but not their mouth. If blankets are not available, you should use your body heat to warm them. If the person is in a conscious state, ask them to take warm beverages or soup to help increase the body temperature.
Apply warm compresses
You may apply a warmed water bottle, a warmed towel, or any other warm compressor to the chest, neck, or groin. But be careful as the sweltering temperatures can burn the skin or result in cardiac arrest.
Monitor the breathing
Closely monitor the person’s breathing and if it seems dangerously slow, or if the individual loses consciousness, perform CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) if you know how to do it.
Medications
Medical treatments such as warm fluids, usually saline, are injected into the veins. Your medical healthcare provider may rewarm your blood, a method in which they draw blood, warm them, and place it back into the body.
Airway rewarming is also possible through masks and nasal tubes. Warming the stomach with the help of a cavity lavage or abdomen pump, where warm saltwater solution pumps into the stomach, can prove beneficial.